Reverse ssh : Accéder à un serveur derrière un NAT - Firewall : Différence entre versions
De wikiGite
| Ligne 36 : | Ligne 36 : | ||
| − | Créer un script dans /etc/init.d/autosshd | + | Créer un script dans /etc/init.d/autosshd et remplacer les variables REMOTE_ADDR et LISTEN_PORT : |
<source lang="bash"> | <source lang="bash"> | ||
| Ligne 42 : | Ligne 42 : | ||
| − | |||
DAEMON="/usr/bin/autossh" | DAEMON="/usr/bin/autossh" | ||
DESC="Autossh daemon" | DESC="Autossh daemon" | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
REMOTE_USER="userssh" | REMOTE_USER="userssh" | ||
| − | REMOTE_ADDR=" | + | REMOTE_ADDR="test.systea.fr" |
| + | LISTEN_PORT="22222" | ||
LOGFILE="/var/log/autossh.log" | LOGFILE="/var/log/autossh.log" | ||
| − | + | export AUTOSSH_PIDFILE=/tmp/$REMOTE_USER-$REMOTE_ADDR.pid | |
| − | + | AUTOSSH_PIDFILE="/tmp/$REMOTE_USER-$REMOTE_ADDR.pid" | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
test -f $DAEMON || exit 0 | test -f $DAEMON || exit 0 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
is_running() { | is_running() { | ||
| − | if [ -f $ | + | if [ -f $AUTOSSH_PIDFILE ]; then |
| − | PID=`cat $ | + | PID=`cat $AUTOSSH_PIDFILE` |
if [ -n "$PID" ]; then | if [ -n "$PID" ]; then | ||
return 0 | return 0 | ||
| Ligne 81 : | Ligne 68 : | ||
start_autossh() { | start_autossh() { | ||
if ! is_running; then | if ! is_running; then | ||
| − | echo "Starting $DESC" | + | echo -n "Starting $DESC" |
| − | + | $DAEMON -i /root/.ssh/id_dsa -NR $LISTEN_PORT:localhost:22 $REMOTE_USER@$REMOTE_ADDR >> $LOGFILE 2>&1 & | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
sleep 1; | sleep 1; | ||
| − | if | + | if is_running; then |
| − | echo " | + | echo " [DONE] : Running @ pid $PID " |
else | else | ||
| − | echo ' | + | echo '[FAIL]'; |
fi | fi | ||
else | else | ||
| − | echo " | + | echo "Already running (pid $PID)" |
fi | fi | ||
} | } | ||
| Ligne 99 : | Ligne 83 : | ||
stop_autossh() { | stop_autossh() { | ||
if is_running; then | if is_running; then | ||
| − | echo "Stopping $DESC" | + | echo -n "Stopping $DESC: " |
| − | + | kill -s SIGTERM $PID | |
| − | + | echo "[DONE]" | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
else | else | ||
| − | echo " | + | echo "[FAIL] : Not running " |
fi | fi | ||
| − | [ -f $ | + | [ -f $AUTOSSH_PIDFILE ] && rm -f $AUTOSSH_PIDFILE |
} | } | ||
| Ligne 129 : | Ligne 109 : | ||
else | else | ||
echo "$DESC: not running" | echo "$DESC: not running" | ||
| − | [ -f $ | + | [ -f $AUTOSSH_PIDFILE ] && exit 1 || exit 3 |
fi | fi | ||
;; | ;; | ||
log) | log) | ||
| − | if [ -f $ | + | if [ -f $LOGFILE ]; then |
tail $LOGFILE | tail $LOGFILE | ||
else | else | ||
| − | echo "log file '$LOGFILE' does't exist" | + | echo "[FAIL] : log file '$LOGFILE' does't exist" |
fi | fi | ||
;; | ;; | ||
Version du 25 avril 2012 à 15:49
Sommaire
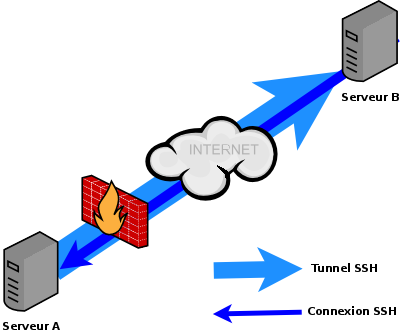
Fonctionnement
Le serveur A se trouvant derriere le par-feu créé un tunnel vers le serveur B. Depuis B on se connecte au serveur A au travers du tunnel ssh.
Prérequis
Ajouter cette ligne dans /etc/ssh/sshd_config :
AllowTcpForwarding yes
Par sécurité créer un utilisateur dédié au tunnel sur B :
adduser userssh
Reverse ssh
Le port 22222 de l'exemple suivant doit se trouver entre 1024 et 65535. Il faut evidement tenir une liste des ports accociés aux machines.
Créez le tunnel sur le serveur A :
ssh -NR 22222:localhost:22 userssh@serveurB
Se connecter au tunnel depuis le serveur B
ssh -p 22222 rootA@127.0.0.1
Service au démarrage de A
aptitude install autossh
Générer une paire de clef avec root
ssh-keygen -t dsa
Faire un echange de clef avec le serveur B:
ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_dsa.pub userssh@serveurB
ajouter dans /etc/rc.local :
autossh -i /root/.ssh/id_dsa -NR 22222:localhost:22 userssh@serveurB &
Créer un script dans /etc/init.d/autosshd et remplacer les variables REMOTE_ADDR et LISTEN_PORT :
#!/bin/bash
DAEMON="/usr/bin/autossh"
DESC="Autossh daemon"
REMOTE_USER="userssh"
REMOTE_ADDR="test.systea.fr"
LISTEN_PORT="22222"
LOGFILE="/var/log/autossh.log"
export AUTOSSH_PIDFILE=/tmp/$REMOTE_USER-$REMOTE_ADDR.pid
AUTOSSH_PIDFILE="/tmp/$REMOTE_USER-$REMOTE_ADDR.pid"
test -f $DAEMON || exit 0
is_running() {
if [ -f $AUTOSSH_PIDFILE ]; then
PID=`cat $AUTOSSH_PIDFILE`
if [ -n "$PID" ]; then
return 0
else
return 1
fi
else
return 1
fi
}
start_autossh() {
if ! is_running; then
echo -n "Starting $DESC"
$DAEMON -i /root/.ssh/id_dsa -NR $LISTEN_PORT:localhost:22 $REMOTE_USER@$REMOTE_ADDR >> $LOGFILE 2>&1 &
sleep 1;
if is_running; then
echo " [DONE] : Running @ pid $PID "
else
echo '[FAIL]';
fi
else
echo "Already running (pid $PID)"
fi
}
stop_autossh() {
if is_running; then
echo -n "Stopping $DESC: "
kill -s SIGTERM $PID
echo "[DONE]"
else
echo "[FAIL] : Not running "
fi
[ -f $AUTOSSH_PIDFILE ] && rm -f $AUTOSSH_PIDFILE
}
case "$1" in
start)
start_autossh
;;
stop)
stop_autossh
;;
force-reload|restart)
stop_autossh
start_autossh
;;
status)
if is_running; then
echo "$DESC: running (pid $PID)"
exit 0
else
echo "$DESC: not running"
[ -f $AUTOSSH_PIDFILE ] && exit 1 || exit 3
fi
;;
log)
if [ -f $LOGFILE ]; then
tail $LOGFILE
else
echo "[FAIL] : log file '$LOGFILE' does't exist"
fi
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|force-reload|status|log}"
exit 3
;;
esac
exit 0
Autoriser l'execution du script :
chmod +x /etc/init.d/autosshd
Ajouter le script au démarage :
update-rc.d autosshd defaults
Se connecter à d'autres port
On souhaite par exemple se connecter à un serveur web se trouvant sur A.
Sur A :
ssh -NR 22280:localhost:80 userssh@serveurB
Sur B :
firefox "http://127.0.0.1:22280"