Mod Proxy : Différence entre versions
De wikiGite
(→Création d'un virtual host sur le proxy) |
(→Principe de fonctionnement en mode Reverse-Proxy) |
||
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
| − | == Principe de fonctionnement | + | == Principe de fonctionnement == |
| − | http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.3/mod/mod_proxy.html | + | *<u> Doc. Apache </u> : http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.3/mod/mod_proxy.html |
| + | *<u> Doc. Developpez.com </u> : http://julien-pauli.developpez.com/tutoriels/web/http/?page=page_7 | ||
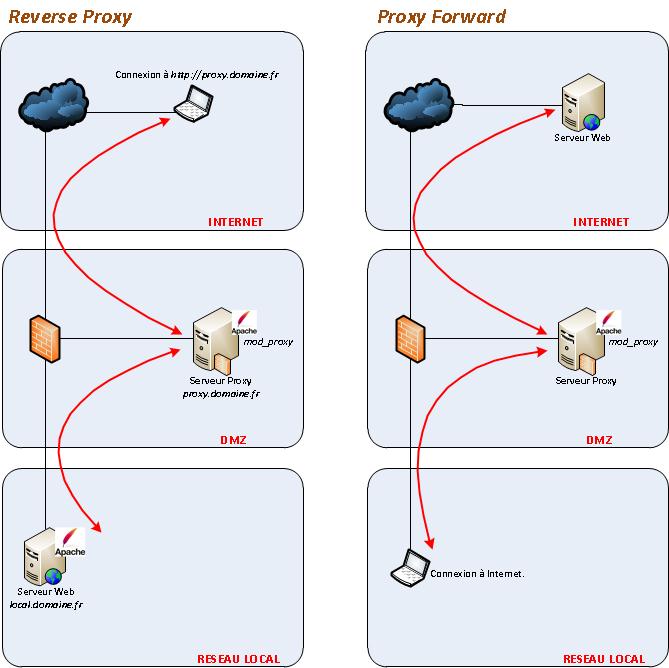
| − | L'utilisation d'Apache mod_proxy (reverse-proxy) permet aux utilisateurs externes d'accéder à un serveur Web interne (dans un LAN derrière un pare-feu) via un serveur proxy (situé en DMZ). | + | 2 modes de fonctionnement : |
| + | *Proxy-Forward : | ||
| + | Les utilisateurs situés dans un réseau local accèdent à un serveur Web situé sur Internet par l'intermédiaire du serveur proxy. Ils doivent donc obligatoirement passer par le proxy pour aller sur Internet. | ||
| + | *Reverse-Proxy : | ||
| + | L'utilisation d'Apache mod_proxy (reverse-proxy) permet aux utilisateurs externes d'accéder à un serveur Web interne (dans un LAN derrière un pare-feu) via un serveur proxy (situé en DMZ). | ||
[[Fichier:Apache_Proxy.jpg]] | [[Fichier:Apache_Proxy.jpg]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Pré-Requis == | == Pré-Requis == | ||
Version du 8 juillet 2011 à 09:34
Sommaire
Principe de fonctionnement
- Doc. Apache : http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.3/mod/mod_proxy.html
- Doc. Developpez.com : http://julien-pauli.developpez.com/tutoriels/web/http/?page=page_7
2 modes de fonctionnement :
- Proxy-Forward :
Les utilisateurs situés dans un réseau local accèdent à un serveur Web situé sur Internet par l'intermédiaire du serveur proxy. Ils doivent donc obligatoirement passer par le proxy pour aller sur Internet.
- Reverse-Proxy :
L'utilisation d'Apache mod_proxy (reverse-proxy) permet aux utilisateurs externes d'accéder à un serveur Web interne (dans un LAN derrière un pare-feu) via un serveur proxy (situé en DMZ).
Pré-Requis
- Un serveur situé dans la DMZ avec apache2
- Le serveur Web situé dans le réseau local avec apache2 et un vhost accessible
- Dans le pare-feu, le port 80 (par exemple) doit être autorisé entre le proxy et le serveur Web interne
Activation du module mod_proxy sur le proxy
a2enmod proxy
/etc/init.d/apache2 restart
Création d'un virtual host <nom_du_vhost> sur le proxy
Créer le fichier <nom_du_vhost> dans /etc/apache2/sites-available/ avec le contenu suivant (où ProxyPass pointe vers un vhost du serveur Web local) :
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName proxy.domaine.fr
<Location />
ProxyPass http://local.domaine.fr/
</Location>
</VirtualHost>
a2ensite <nom_du_vhost>
/etc/init.d/apache2 restart
# owned by VirtualHost
NameVirtualHost 192.168.1.12:80
# FrontPage needs the following four things to be here
# otherwise all the vhosts need to go in httpd.conf, which could
# get very large since there could be thousands of vhosts
ServerRoot /etc/httpd
<VirtualHost 192.168.1.12:80>
<Location />
ProxyPass http://local.domaine.fr/
</Location>
ServerName proxy.domaine.fr
ServerAdmin admin
#DocumentRoot /home/.sites/28/site1/web
#ErrorDocument 401 /error/401-authorization.html
#ErrorDocument 403 /error/403-forbidden.html
#ErrorDocument 404 /error/404-file-not-found.html
#ErrorDocument 500 /error/500-internal-server-error.html
#RewriteEngine on
#RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^192.168.1.12(:80)?$
#RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^proxy.domaine.fr(:80)?$ [NC]
#RewriteRule ^/(.*) http://proxy.domaine.fr/$1 [L,R=301]
#RewriteOptions inherit
#AliasMatch ^/~([^/]+)(/(.*))? /home/.sites/28/site1/users/$1/web/$3
#Include /etc/httpd/conf/vhosts/site1.include
# BEGIN WebScripting SECTION. DO NOT EDIT MARKS OR IN BETWEEN.
# END WebScripting SECTION. DO NOT EDIT MARKS OR IN BETWEEN.
# BEGIN PHP SECTION. DO NOT EDIT MARKS OR IN BETWEEN.
# END PHP SECTION. DO NOT EDIT MARKS OR IN BETWEEN.
</VirtualHost>
# end of VirtualHost owned section